Spring Cloud Stream
是什么
Spring Cloud Stream是一个构件消息驱动微服务的框架。
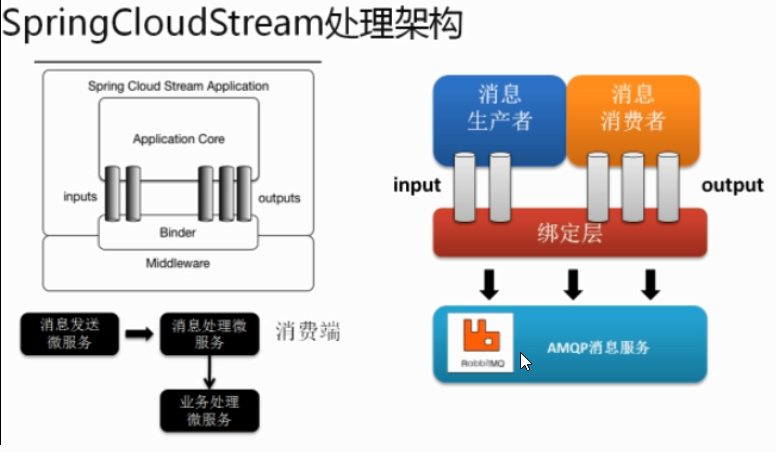
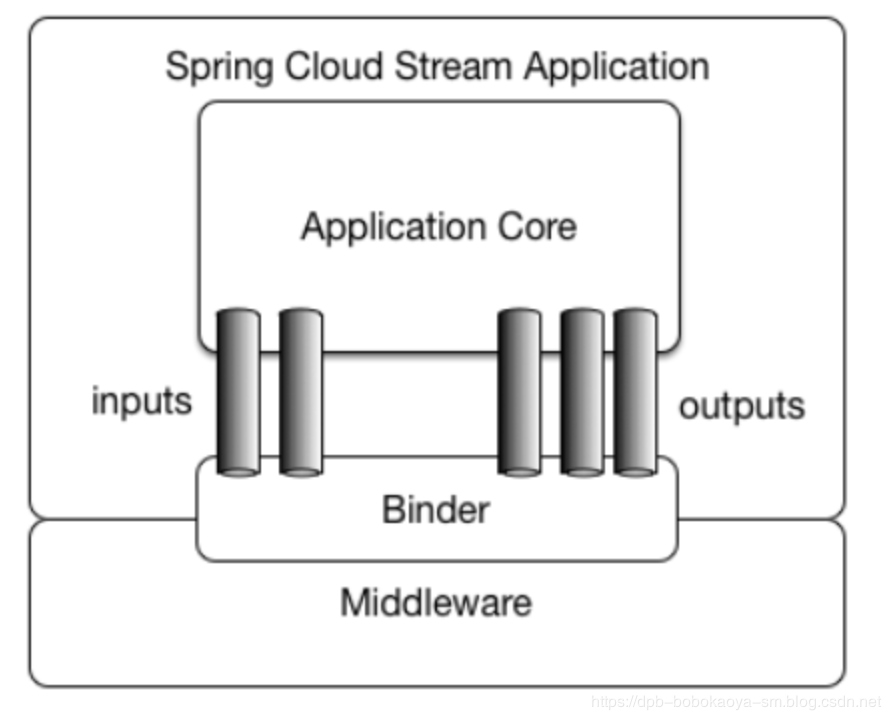
应用程序通过inputs或者outputs来与Spring Cloud Stream中的binder对象交互。通过我们配置binding,Spring Cloud Stream的binder对象负责与消息中间件交互。
通过使用Spring Integration来链接消息代理中间件以实现消息事件驱动。Spring Cloud Stream为一些供应商的消息中间件产品提供了个性化的自动化配置实现,引用了发布-订阅、消费组、分区的三个核心概念。
官方文档
在没有绑定器这个概念的情况下,SpringBoot应用要直接与消息中间件进行信息交互的时候,由于各个消息中间件构建的初衷不同,他们的实现细节会有较大的差异,通过定义绑定器作为中间件,完美地实现了应用程序与消息中间件细节之间的隔离,通过向应用程序暴露统一的Channel通道,使得应用程序不需要再考虑各种不同的消息中间件实现。
spring官方目前只支持RabbitMQ和Kafka,rocketMQ的由alibaba研发支持。
设计思想
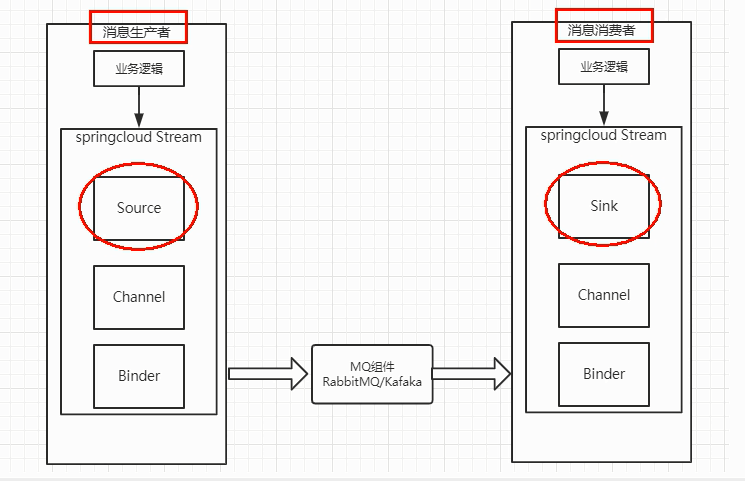
Binder :很方便的链接中间件,屏蔽差异
Channel:通道,是队列queue的一种抽象,在消息通讯系统中就是实现存储和转发的媒介,通过Cahnnel对队列进行配置。
Source和Sink:参照对象是Spring Cloud Stream自身,从Stream发布消息就是输出,接受消息就是输入。
| 组成 |
说明 |
| Middleware |
中间件,目前只支持RabbitMQ和Kafka |
| Binder |
Binder是应用与消息中间件之间的封装,目前实行了Kafka和RabbitMQ的Binder,通过Binder可以很方便的连接中间件,可以动态的改变消息类型(对应于Kafka的topic,RabbitMQ的exchange),这些都可以通过配置文件来实现 |
| @Input |
注解标识输入通道,通过该输入通道接收到的消息进入应用程序 |
| @Output |
注解标识输出通道,发布的消息将通过该通道离开应用程序 |
| @StreamListener |
监听队列,用于消费者的队列的消息接收 |
| @EnableBinding |
指信道channel和exchange绑定在一起 |
生产者
新建springBoot工程cloud-stream-privider
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-rocketmq</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| server:
port: 8801
spring:
application:
name: cloud-stream-rocketmq-provider
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848
config:
server-addr: localhost:8848
file-extension: yaml
stream:
rocketmq:
binder:
name-server: localhost:9876
bindings:
output:
destination: testChannel
|
1
2
3
4
| package cn.midkuro.com.service;
public interface ProviderService {
void send(String message);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.EnableBinding;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.messaging.Source;
import org.springframework.messaging.MessageChannel;
import org.springframework.messaging.support.MessageBuilder;
@EnableBinding(Source.class) //定义消息推送通道
public class ProviderServiceImpl implements ProviderService {
@Autowired
private MessageChannel output;
@Override
public String send() {
String serial = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
output.send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(serial).build());
System.out.println("***********serial:"+serial);
return serial;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @RestController
@RefreshScope
public class ProviderController {
@Autowired
private ProviderService service;
@GetMapping("/sendMessage")
public void sendMessage() {
service.send();
}
}
|
消费者
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| server:
port: 8802
spring:
application:
name: cloud-stream-rocketmq-consumer
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848
config:
server-addr: localhost:8848
file-extension: yaml
stream:
rocketmq:
binder:
name-server: localhost:9876
bindings:
input:
destination: testChannel
group: cloud-stream-rocketmq-consumer
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| package cn.midkuro.com.Service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.EnableBinding;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.annotation.StreamListener;
import org.springframework.cloud.stream.messaging.Sink;
import org.springframework.messaging.Message;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@EnableBinding(Sink.class)
public class ConsumerService {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String serverPort;
@StreamListener(Sink.INPUT)
public void input(Message<String> message) {
System.out.println("我是消费者1号,-----》接受到的消息是:" + message.getPayload() + "\t" + serverPort);
}
}
|
自定义Binding
org.springframework.cloud.stream.binder.Binder是Spring Cloud对消息容器的抽象,不同的消息容器有不同的实现,通过它可以屏蔽各消息容器的内部细节。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public interface Binder<T, C extends ConsumerProperties, P extends ProducerProperties> {
Binding<T> bindConsumer(String name, String group, T inboundBindTarget,
C consumerProperties);
Binding<T> bindProducer(String name, T outboundBindTarget, P producerProperties);
}
|
Binder可以生成Binding,Binding用来绑定消息容器的生产者和消费者。
它有两种类型,INPUT和OUTPUT,INPUT对应于消费者,OUTPUT对应于生产者。
可以通过在配置类上使用@EnableBinding指定需要使用的Binding,它指定的是一个接口,在对应接口中会定义一些标注了@Input或@Output的方法,它们就对应一个Binding了。
Spring提供了两个内置的接口,Source和Sink,Source对应的是OUTPUT生产者,Sink对应的是INPUT消费者。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public interface Source {
String OUTPUT = "output";
@Output(Source.OUTPUT)
MessageChannel output();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public interface Sink {
String INPUT = "input";
@Input(Sink.INPUT)
SubscribableChannel input();
}
|
在一个EnableBinding注解中可以同时定义多个Binding,如下:
1
2
3
| @EnableBinding(value = { Source.class, Sink.class })
//或者
@EnableBinding(Processor.class)
|
1
2
| public interface Processor extends Source, Sink {
}
|
默认情况下,它的内置binding是input和output,也就是我们配置文件配置的:
1
2
3
4
5
| spring:
cloud:
stream:
bindings:
output:
|
如果自定义了一个binding配置,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
| spring:
cloud:
stream:
bindings:
mybinding: #自定义绑定器名称
|
1
2
3
4
5
| public interface MyBinding {
@Output("mybinding")
MessageChannel output();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @EnableBinding(MyBinding.class)
public class ProviderServiceImpl implements ProviderService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("mybinding")
private MessageChannel output;
}
|
若是消费者频道,则是在方法上通过@StreamListener进行标注,表示它将监听消费某个Binding的消息。
1
| @StreamListener("mybinding")
|
当有多个Binding时,可以通过进行组合,并在使用注入时通过@Qualifier进行区分即可,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public interface MutipleMyBinding {
@Output("mybinding1")
MessageChannel output1();
@Output("mybinding2")
MessageChannel output2();
}
|
重复消费
比如在如下场景中,订单系统做集群部署,都会从消息队列中获取订单信息,那如果一个订单同时被两个服务获取到,就会造成数据错误,得避免这种情况,这时候需要使用stream中的消息分组来解决。
在stream中处于同一个group中的多个消费者是竞争关系,就能保证消息只会被其中一个应用消费一次。不同组是可以全面消费的(重复消费)。
微服务应用放置于同一个group中,就能够保证消息只会被其中一个应用消费一次。不同的组是可以重复消费的,同一个组内会发生竞争关系,只有一个可以消费。
通过在配置文件配置分组配置实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
| spring:
cloud:
stream:
bindings:
input:
group: myGroupName
|
持久化
配置了分组名称的消费者,在程序重新启动时,会接着消费未消费的消息,而没有配置分组的,则会丢失之前未消费的消息。




